There are two ways to know when an element gets visible / hidden in the screen during scrolling:
- Listening to the window scroll event
- Observing the element for visibility using Intersection Observer API
Listening to the scroll Event
Attach a scroll event handler to the window object, and use getBoundingClientRect() to calculate the position of the element relative to the viewport.
- top: distance from the top of the viewport
- bottom: distance from the bottom of the viewport
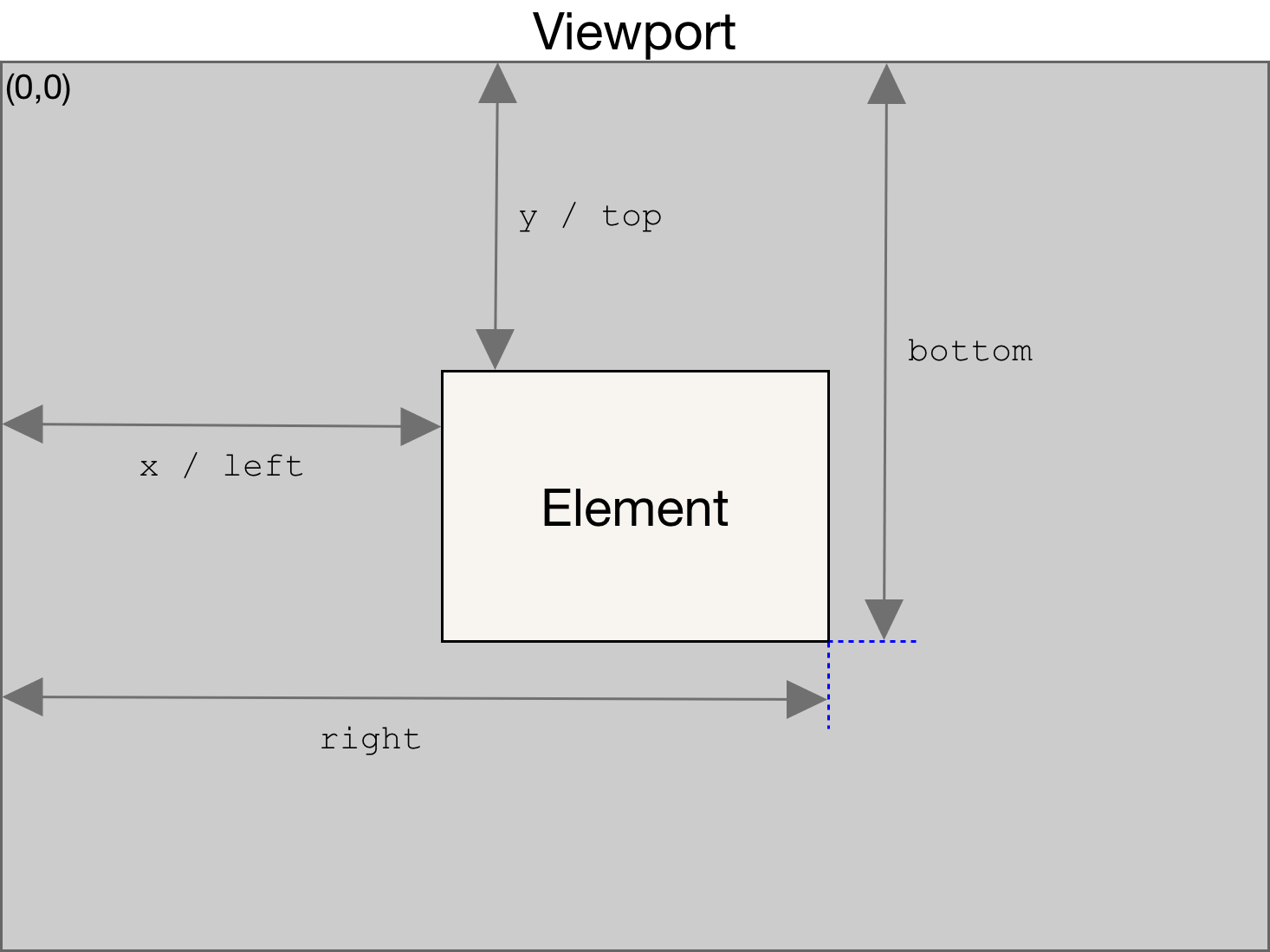
- positive value -> below the top of the screen
- negative value -> above the top of the screen
- scroll events have a lot of performance issues.
window.addEventListener('scroll', function() {
var element = document.querySelector('#main-container');
var position = element.getBoundingClientRect();
// checking whether fully visible
if(position.top >= 0 && position.bottom <= window.innerHeight) {
console.log('Element is fully visible in screen');
}
// checking for partial visibility
if(position.top < window.innerHeight && position.bottom >= 0) {
console.log('Element is partially visible in screen');
}
});Intersection Observer API
- This API is asynchronous
- Calculate intersection between a target element and the browser viewport
- Threshold is a number between 0 and 1, that represents the viewable area of the target element in the screen (threshold to 0.10, callback function will be invoked every time when viewable area becomes greater than 10% or becomes less than 10% )
var observer = new IntersectionObserver(function(entries) {
// isIntersecting is true when element and viewport are overlapping
// isIntersecting is false when element and viewport don't overlap
if(entries[0].isIntersecting === true)
console.log('Element has just become visible in screen');
}, { threshold: [0] });
observer.observe(document.querySelector("#main-container"));https://usefulangle.com/post/113/javascript-detecting-element-visible-during-scroll